Read Also: IllegalArgumentException in Java with Examples
[Fixed] java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException
Example 1: Producing the exception by using %d format specifier for double data type
We can easily produce this exception by using integer(%d) format specifier for double data type as shown below:
public class IllegalFormatConversionExceptionExample { public static void main(String args[]) { // Initializing variables int x=10; double y=25; /* Below line will throw IllegalFormatConversionException as we are trying to print "y" double data type with %d(integer) format specifier */System.out.printf("%d, %d ",x,y);} }
Output:
10,
Exception in thread "main" java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException: d != java.lang.Double
Explanation:
The cause of this error is due to the format specifier of incompatible types. %d is used for integer in Java. Variable y is of double data type. In the above example, we were using %d for the double data type. As a result, we were getting java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException.Solution:
The above runtime exception can be resolved by replacing %d format specifier with %f as shown below:public class IllegalFormatConversionExceptionExample { public static void main(String args[]) { // Initializing variables int x=10; double y=25; /* Below line will not throw IllegalFormatConversionException as we are trying to print "y" double data type with %f format specifier */System.out.printf("%d, %f ",x,y);} }
Output:
10, 25.000000
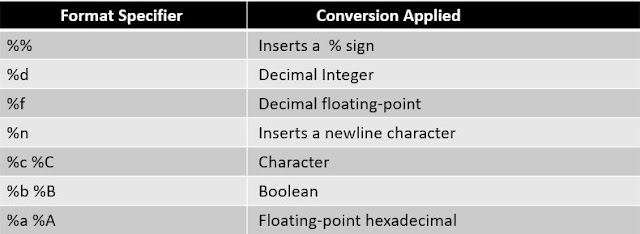
Conversions
Example 2: Producing the exception by using %c format specifier for boolean data type
We can easily produce this exception by using character(%c) format specifier for boolean data type as shown below:
public class IllegalFormatConversionExceptionExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { // Initializing variables int x=10; boolean y = true; /* Below line will throw IllegalFormatConversionException as we are trying to print "y" boolean data type with %c(character) format specifier */System.out.printf("%d, %c ",x,y);} }
Output:
10,
Exception in thread "main" java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException: c != java.lang.Boolean
Explanation:
Just like example 1, the cause of this error is due to the format specifier of incompatible types. %c is used for the character in Java. Variable y is of boolean data type. In the above example, we were using %c for the boolean data type. Hence, we were getting java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException.Solution:
The above runtime exception can be resolved by replacing %c format specifier with %b as shown below:public class IllegalFormatConversionExceptionExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { // Initializing variables int x=10; boolean y = true; /* Below line will not throw IllegalFormatConversionException as we are trying to print "y" boolean data type with %b(boolean) format specifier */System.out.printf("%d, %b ",x,y);} }
Output:
10, true
That's all for today. Please mention in the comments in case you are still facing the exception java.util.IllegalFormatConversionException in Java.