A calculator is a small, portable, often inexpensive electronic device used to perform both basic and complex operations of arithmetic.
Here in this program we will create a console based calculator . Anyone can perform the basic operations in the calculator , i.e add , subtract , multiply , divide .
Here user needs ti input the two numbers and then need to press the number corresponding to the particular
operation .
Read also : How to Create Random number in Java
Things to learn in this code
Scanner scan= new Scanner(System.in)
//sets up scanner string
action=scan.nextLine();
//This is the code to read the inputs of the user from the console . Here System is the java class and in is the variable which means input .
It is good practice to flush the object of the scanner class in the end of the class . Scanner class is mainly use to read the user inputs from the console . Although one can also use Console java class to achieve the same , but here we use scanner object .
To do it through console class ,We need to create the console class object
Console console= System.console();
then read through each line through readLine() method
String line = console.readLine();
Pseudo Code :
1. Menu is shown to select the operation
2. If user inputs a
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
else if user inputs s
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
else if user inputs m
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
else if user inputs d
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
3. Show the result
Read Also : Square root java swing code with example
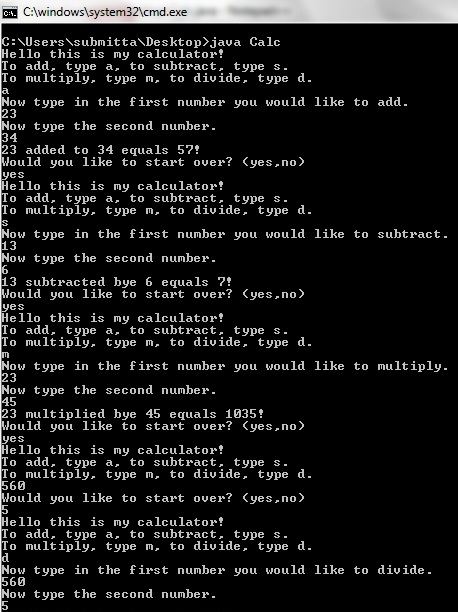
Demo
Please find the code below :
Here in this program we will create a console based calculator . Anyone can perform the basic operations in the calculator , i.e add , subtract , multiply , divide .
Here user needs ti input the two numbers and then need to press the number corresponding to the particular
operation .
Read also : How to Create Random number in Java
Things to learn in this code
Scanner scan= new Scanner(System.in)
//sets up scanner string
action=scan.nextLine();
//This is the code to read the inputs of the user from the console . Here System is the java class and in is the variable which means input .
It is good practice to flush the object of the scanner class in the end of the class . Scanner class is mainly use to read the user inputs from the console . Although one can also use Console java class to achieve the same , but here we use scanner object .
To do it through console class ,We need to create the console class object
Console console= System.console();
then read through each line through readLine() method
String line = console.readLine();
Pseudo Code :
1. Menu is shown to select the operation
2. If user inputs a
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
else if user inputs s
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
else if user inputs m
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
else if user inputs d
then prompt the user to input the first number and second number
3. Show the result
Read Also : Square root java swing code with example
Demo
Please find the code below :
import java.util.Scanner; //imports scanners public class Calc { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean go = true; //sets up loop while(go) //creates loop to top { System.out.println("Hello this is my calculator!"); System.out.println("To add, type a, to subtract, type s."); System.out.println("To multiply, type m, to divide, type d."); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); //sets up scanners Scanner scan1 = new Scanner(System.in); String action = scan.nextLine(); //tells comp. to take user input if("a".equals(action)) //addition { System.out.println("Now type in the first number you would like to add."); int add1 = scan.nextInt(); System.out.println("Now type the second number."); int add2 = scan.nextInt(); int add3 = add1 + add2; System.out.println(add1 + " added to " + add2 + " equals " + add3 + "!"); } if("s".equals(action)) //subtraction { System.out.println("Now type in the first number you would like to subtract."); int sub1 = scan.nextInt(); System.out.println("Now type the second number."); int sub2 = scan.nextInt(); int sub3 = sub1 - sub2; System.out.println(sub1 + " subtracted bye " + sub2 + " equals " + sub3 + "!"); } if("m".equals(action)) //multiplacation { System.out.println("Now type in the first number you would like to multiply."); int mul1 = scan.nextInt(); System.out.println("Now type the second number."); int mul2 = scan.nextInt(); int mul3 = mul1 * mul2; System.out.println(mul1 + " multiplied bye " + mul2 + " equals " + mul3 + "!"); } if("d".equals(action)) //division { System.out.println("Now type in the first number you would like to divide."); int div1 = scan.nextInt(); System.out.println("Now type the second number."); int div2 = scan.nextInt(); int div3 = div1 / div2; System.out.println(div1 + " divided bye " + div2 + " equals " + div3 + "!"); } System.out.println("Would you like to start over? (yes,no)"); String startOver = scan1.nextLine(); if("no".equals(startOver)) { go = false; System.out.println("Bye"); } } } }